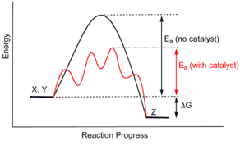
 Hydrogen peroxide oxidises potassium sodium tartrate (Rochelle salt) to carbon dioxide. The reaction is catalysed by cobalt(II) chloride.
Hydrogen peroxide oxidises potassium sodium tartrate (Rochelle salt) to carbon dioxide. The reaction is catalysed by cobalt(II) chloride.
When solutions of hydrogen peroxide and Rochelle salt are mixed, carbon dioxide is slowly evolved. The addition of cobalt(II) chloride causes the reaction to froth, indicating a large increase in the reaction rate.
At the same time the colour of the cobalt(II) chloride turns from pink to green (an activated complex), returning to pink again within a few seconds as the reaction dies down.
This indicates the catalysts actually take part in the reaction and are returned unchanged when the reaction is complete.



